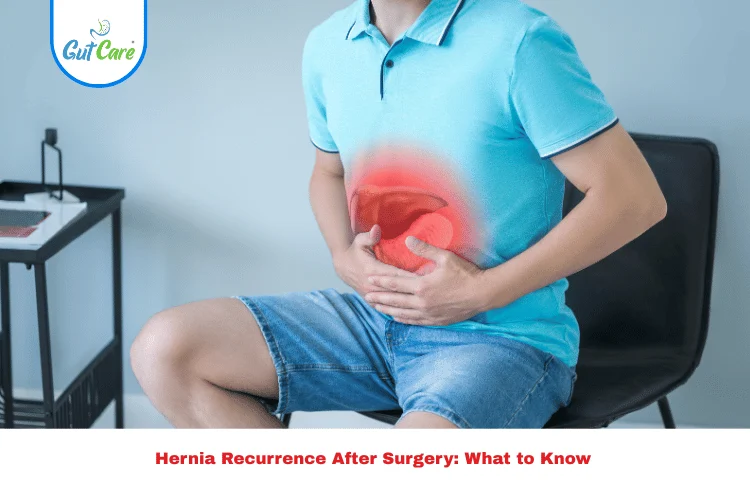
Living with a stoma is a big adjustment, and while it can greatly improve health and quality of life, some people may experience a complication known as a parastomal hernia. This condition happens when a portion of the intestine pushes through the abdominal wall near the stoma site, creating a bulge.
At Gutcare Clinics in Bangalore, patients often come in worried about swelling or discomfort around their stoma. They ask: Why is this happening, and what can be done about it? In this article, we’ll explain the causes, the treatment options including parastomal hernia repair, and when to seek help from a specialist like Dr. Yuvrajsingh Gehlot.
What Is a Parastomal Hernia?
A parastomal hernia is one of the most common complications after stoma surgery. It develops when the intestine or other tissue bulges through the abdominal wall, right next to the stoma opening.
Not everyone with a stoma will develop a hernia, but studies suggest that up to 50% of stoma patients experience it at some point. While some hernias cause only minor discomfort, others can lead to more serious problems that require medical attention.
Parastomal Hernia Causes
Understanding causes can help in both prevention and treatment. Some of the most common reasons include:
- Surgical factors: The size and location of the stoma opening play a role. Larger openings tend to increase hernia risk.
- Weak abdominal muscles: If the abdominal wall is naturally weak or becomes weaker over time, hernias are more likely.
- Obesity: Extra weight increases pressure inside the abdomen.
- Chronic coughing or straining: Long-term coughing, constipation, or heavy lifting can all put stress on the abdominal wall.
- Age: As we age, muscles and connective tissues lose strength, making hernias more common.
These causes don’t mean every stoma patient will develop a hernia, but being aware of them helps in taking preventive steps.
Common Symptoms
A parastomal hernia often shows up as a swelling or bulge near the stoma site. Other symptoms may include:
- Discomfort or dull pain around the stoma
- Difficulty keeping the stoma appliance in place
- Changes in stoma function or pouch leaks
- A heavy or dragging feeling in the abdomen
- In severe cases, bowel obstruction (nausea, vomiting, or inability to pass stool)
If you ever notice sudden, severe pain with nausea or vomiting, seek urgent medical help — this could mean the hernia is blocking your bowel.
Diagnosis
Doctors usually diagnose a parastomal hernia with a simple physical examination. Sometimes imaging tests like a CT scan or ultrasound are used for a clearer picture.
At Gutcare Clinics, Dr. Yuvrajsingh Gehlot combines careful clinical evaluation with imaging when needed, ensuring patients get an accurate diagnosis and the right treatment plan.
Treatment Options
The treatment for a parastomal hernia depends on how severe it is and how much it affects daily life.
1. Non-Surgical Management
For mild cases, doctors may recommend:
- Hernia support belts or binders to ease discomfort.
- Lifestyle changes such as weight loss, avoiding heavy lifting, and stopping smoking.
- Appliance adjustments with guidance from a stoma nurse to improve pouch fitting.
These measures don’t fix the hernia but can make living with it easier.
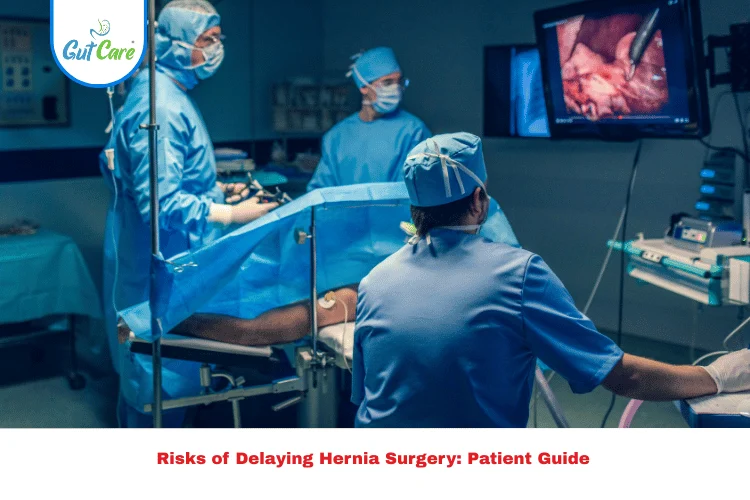
2. Surgical Treatment (Parastomal Hernia Repair)
When symptoms are severe or quality of life is affected, parastomal hernia repair may be necessary. Surgical options include:
- Suture repair: The opening is stitched closed, though recurrence is common.
- Mesh repair: A mesh is placed to strengthen the abdominal wall — currently the most effective method.
- Stoma relocation: Moving the stoma to a new spot on the abdomen if repair isn’t feasible.
The choice of surgery depends on the patient’s health, hernia size, and overall goals.
Prevention Tips
While hernias cannot always be avoided, you can lower your risk by:
- Maintaining a healthy body weight
- Using a stoma support garment when exercising or lifting
- Practicing proper coughing and lifting techniques
- Following all post-surgery instructions carefully
- Staying physically active to strengthen abdominal muscles
Conclusion
A parastomal hernia can be frustrating and uncomfortable, but it doesn’t have to take over your life. By understanding the causes of parastomal hernia, recognizing symptoms early, and exploring treatments such as parastomal hernia repair, patients can manage this condition effectively.
If you are experiencing persistent bulging, pain, or problems with your stoma appliance, don’t ignore it. Reach out to Gutcare Clinics in Bangalore and consult with Dr. Yuvrajsingh Gehlot. The right advice and timely treatment can make a huge difference in comfort, confidence, and overall health.
FAQs
1. What are the main causes of a parastomal hernia?
The most common parastomal hernia causes include weak abdominal muscles, surgical factors, obesity, chronic coughing, and aging.
2. Do all parastomal hernias require surgery?
No. Mild cases can often be managed with support belts, weight control, and appliance adjustments. Surgery is only needed when symptoms become severe or quality of life is affected.
3. What happens during parastomal hernia repair?
Parastomal hernia repair usually involves reinforcing the abdominal wall with mesh, or in some cases relocating the stoma. It helps reduce pain and appliance issues.
4. Where can I find a specialist for parastomal hernia in Bangalore?
At Gutcare Clinics Bangalore, Dr. Yuvrajsingh Gehlot specializes in diagnosing and treating parastomal hernias with both non-surgical and surgical options.
5. Can lifestyle changes help prevent a parastomal hernia?
Yes. Maintaining a healthy weight, using support garments, avoiding heavy lifting, and quitting smoking can all reduce the risk of developing or worsening a parastomal hernia.