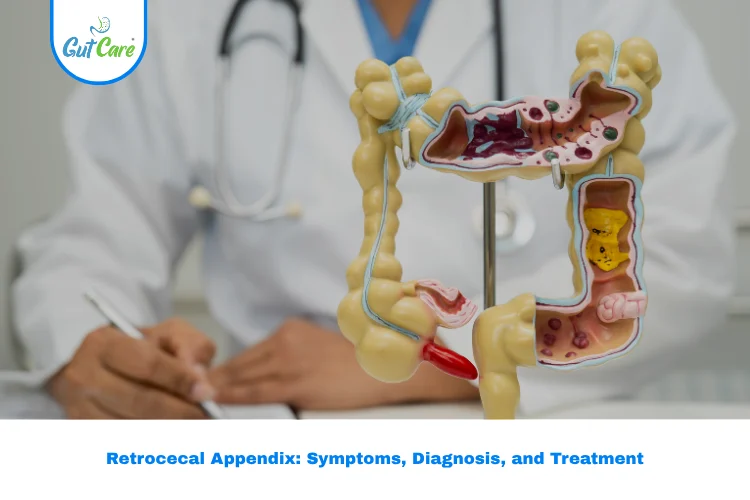
The Retrocecal Appendix is one of the most common positions of the appendix found in humans. Understanding its structure, function, and possible complications is essential for early diagnosis and effective treatment. At Gutcare Clinics in Bangalore, Dr. Yuvrajsingh Gehlot, an experienced colorectal surgeon, provides expert evaluation and care for patients experiencing appendix-related pain and disorders.
The Retrocecal Appendix lies behind the cecum, a part of the large intestine. Because of its location, inflammation in this area often presents with subtle or misleading symptoms, making diagnosis slightly challenging. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a Retrocecal Appendix early can help prevent complications such as perforation or abscess formation.
Retrocecal Appendix Definition
The Retrocecal Appendix is the position of the appendix when it lies behind the cecum in the abdominal cavity. It is one of the five common positions of the appendix others include pelvic, subcecal, preileal, and postileal. When the appendix becomes inflamed in this position, it can cause discomfort that differs from typical appendicitis pain, often radiating toward the back or flank area.
Function of Appendix in Human Body
Though long considered a vestigial organ, modern research has shown that the function of the appendix in the human body plays a role in maintaining gut health. It contains lymphoid tissue that supports immune function and acts as a “safe house” for beneficial gut bacteria. When this organ becomes blocked or infected, however, it can lead to appendicitis, including Retrocecal Appendicitis, which requires medical attention.
Causes of Retrocecal Appendix Inflammation
Several factors can lead to inflammation or infection of the appendix:
- Blockage of the appendix lumen by fecal matter (fecolith) or mucus
- Bacterial infection within the appendix
- Enlarged lymphoid tissue due to infections in the digestive tract
- Trauma or injury near the abdominal region
- Poor gut health or diet, which can cause constipation and stagnation
Signs and Symptoms of Retrocecal Appendix
Because of its unique position, the signs and symptoms of a Retrocecal Appendix can vary from typical appendicitis. Patients may not always experience pain in the lower right abdomen. Instead, discomfort may appear higher or toward the back.
Common symptoms include:
- Dull or sharp pain in the right lower or upper abdomen
- Pain that radiates to the back or flank area
- Nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite
- Mild fever and fatigue
- Abdominal bloating or tenderness
- Discomfort while walking or coughing
In severe cases, the pain may subside temporarily if the appendix ruptures, followed by worsening infection or abscess formation. This makes early medical evaluation critical.
Diagnosis of Retrocecal Appendix
Accurate diagnosis requires a detailed physical examination and imaging tests. At Gutcare Clinics, Dr. Yuvrajsingh Gehlot uses a systematic approach that may include:
- Physical examination: Checking for tenderness and rebound pain
- Ultrasound or CT scan: To identify appendix inflammation or abscess
- Blood tests: To detect elevated white blood cell counts indicating infection
Because symptoms can mimic other abdominal conditions like kidney stones or gallbladder issues, imaging is crucial for proper identification.
Treatment Options for Retrocecal Appendix
Treatment depends on the severity of inflammation and the patient’s overall condition. The main treatment approaches include:
1. Medication and Observation
For mild inflammation detected early, antibiotics and observation may be recommended under strict medical supervision. However, appendicitis rarely resolves completely without surgery.
2. Surgical Treatment
The most common and effective treatment is appendectomy, which involves the removal of the inflamed appendix. Minimally invasive or laparoscopic surgery is preferred as it ensures:
- Faster recovery
- Less postoperative pain
- Minimal scarring
At Gutcare Clinics, Dr. Yuvrajsingh Gehlot performs advanced laparoscopic procedures, ensuring safety and comfort throughout the treatment process.
3. Lifestyle and Preventive Care
To prevent appendix-related issues, maintaining good digestive health is essential:
- Eat fiber-rich foods to avoid constipation
- Stay hydrated
- Avoid processed foods that may irritate the gut
- Get regular medical check-ups for digestive health
When to Consult a Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Persistent abdominal pain
- Fever with nausea or vomiting
- Pain that shifts or increases in intensity
- Sudden relief after severe pain (possible rupture)
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to complications such as peritonitis or abscess formation.
Why Choose Gutcare Clinics, Bangalore
At Gutcare Clinics, the focus is on accurate diagnosis, compassionate care, and advanced treatment. Dr. Yuvrajsingh Gehlot, a skilled colorectal surgeon, specializes in minimally invasive techniques for appendix-related disorders. Each patient receives a customized treatment plan based on their symptoms and health condition.
Gutcare Clinics maintains a hygienic environment, advanced technology, and personalized aftercare, ensuring safe recovery and long-term wellness.
Conclusion
Understanding the Retrocecal Appendix is key to recognizing the early warning signs of inflammation. With proper diagnosis and timely treatment, patients can recover fully and prevent complications. If you suspect symptoms of appendix-related pain, consult Dr. Yuvrajsingh Gehlot at Gutcare Clinics, Bangalore, for expert and compassionate care.
FAQs
1. What is the Retrocecal Appendix?
The Retrocecal Appendix is a type of appendix location where it lies behind the cecum, often causing pain that radiates toward the back or flank instead of the lower right abdomen
2. What are the signs of a Retrocecal Appendix infection?
Common signs include abdominal or back pain, nausea, loss of appetite, mild fever, and tenderness in the right abdomen.
3. How is Retrocecal Appendicitis treated?
Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the appendix (appendectomy), often performed laparoscopically for faster recovery.
4. Can a Retrocecal Appendix cause chronic pain?
Yes, untreated or partially inflamed Retrocecal Appendix can lead to recurring pain or abscess formation that requires medical evaluation.
5. Do Gutcare Clinics treat Retrocecal Appendix cases in Bangalore?
Gutcare Clinics offers advanced diagnosis and surgical care for Retrocecal Appendix cases under the expertise of Dr. Yuvrajsingh Gehlot, a leading colorectal surgeon.